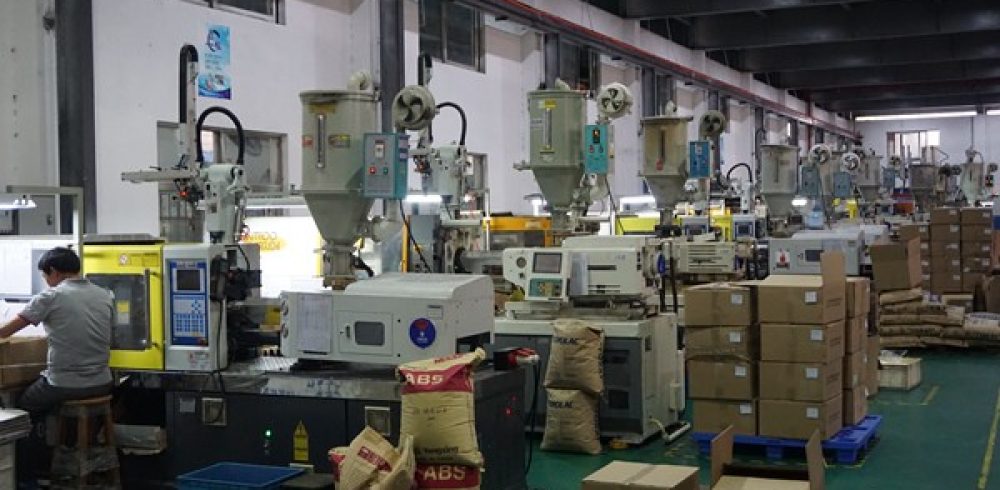
Aluminum Injection Mold – Benefits, Usage, & Challenges : Injection molding is slowly becoming a popular manufacturing process across all industries and is being considered one of the best methods for producing large volumes of parts. Aluminum injection molds are finding applications in consumer electronics, aviation, automotive, and other markets.
Typically employed in mass production, aluminum injection molding can be used to recreate the same part millions of times at a rapid speed. Although this process traditionally uses P20 tool steel, manufacturers are eagerly using aluminum molds because of their reduced cycle time.
Using an aluminum injection mold comes with its own set of benefits and challenges that need to be considered by manufacturers who want to adopt this process for large-scale production.
Why Aluminum Injection Molding is Better Than Traditional Processes
Traditional injection molding processes are lengthy and rely mostly on manual processes. This increases production time as well as labor cost while also leaving room for human error. It leads to flaws in quality which could further cause delays in manufacturing.
In comparison, modern aluminum injection molding is a faster, more accurate process. It is digitized and mostly automated, which eliminates human error and improves production quality. Digital injection molding usually does not require assembly operations and reduces time to market.
With an automated injection molding process, manufacturers can efficiently use assets and reduce labor overhead. It opens up room for the innovation and development of new products to meet the ever-changing market demands.
Aluminum Injection Mold is Superior to Steel Mold
While P-20 tool steel is traditionally used for creating molds, aluminum is a much better option in most aspects. Here are some reasons why manufacturers pick aluminum over steel:
Unlike steel, aluminum is more recyclable and produces lesser scrap, which helps recoup material costs.
CNC aluminum provides up to 10 times faster machining speeds than steel, due to its less dense and softer. This reduces production time and finishing costs by up to 40 percent.
Depending on the grade, aluminum can cost up to 75 percent less than steel.
An aluminum injection mold can last through thousands of production runs.
With aluminum, you get five times faster heat conduction than steel, which ultimately reduces the production time. Better thermal conductivity leads to higher yields and less warpage.
Choosing the Right Aluminum Grade is Crucial
Designing an aluminum injection mold requires several factors to be considered to ensure a successful result. One of these factors is deciding the correct aluminum grade for your particular application.
When choosing an aluminum alloy for creating an rapid tooling, you need to consider the geometry of the part, the resin to be used, the production quantity, the desired cycle time, and the intended estimated number of reuses for the mold.
Different alloys have different characteristics, and different applications and industries demand different aluminum grades. Manufacturers need to choose the right grade for their particular purpose between Series 1000 to Series 7000 aluminum alloys. Sometimes, a little trial and error are needed before finalizing a grade for the mold.
Some commercially available aluminum grades include Hokotol, QC-10, Alumec, Alumold 500, and Bohler 7075. Aluminum molds, if maintained properly, can be used up to a million times.
Consider These Aspects Before Choosing Aluminum Injection Molding
If you are considering using aluminum injection molds for manufacturing parts, here are a few things to keep in mind before you make the decision:
Injection molding of a product demands a hefty initial investment.
Determine if injection molding is the most cost-effective way of producing the number of parts you require.
Make sure the part is specifically designed for the injection molding process.
Use a Moldflow software for designing your mold to avoid defects during manufacturing.
The design of your part should be efficient enough to minimize assembly as much as possible to save production costs.
The Advantages of a Digitized Injection Molding Process
Digitization truly accelerates all manufacturing processes right from designing to creating the final product. Digital manufacturing is extremely flexible and scalable, so the production volume can be modified as per market demand. This saves a lot of time, resources, and money.
With a digital injection molding process, manufacturers can implement design changes quickly and adjust to market behavior changes rapidly. With the integration of CAD software in the process, teams can go through various iterations of a product and come up with innovative designs.
Advice for Using and Maintaining Aluminum Injection Molds Properly
Although every injection molding process is different, here are some basic things you should keep in mind when working with an aluminum injection mold:
During the designing phase itself, it is beneficial to account for any potential design changes that might occur later on. This may prove to be cost-effective in the future and will act as Plan B.
Ensure that your mold is strong enough to survive the molding process to avoid last-minute surprises.
Your mold must be extremely smooth so that the injected part can be ejected cleanly.
Organize your molds in one spot (mold storage) so that you don’t waste time finding the right mold. Along with proper inventorying, it is important to store molds near the press.
Even if most of the process is automated, it is a good practice to follow a production checklist.
When it comes to maintaining injection molds, ensure that they are dismantled and cleaned properly every production run. Typically, you need to follow a thorough cleaning routine every week. After cleaning, it is important to check for galling and/or wear and tear.
Avoid these mistakes with aluminum injection molding:
Excessive injection pressures and temperatures can damage the mold as well as the tool, reducing its life expectancy. Make sure these parameters are monitored closely.
Thorough prototyping is necessary before going into large-scale production to avoid costly mistakes and wastage of resources.
Do not leave the injection mold idle between set-up changes. Instead, you can save time and pre-stage the next changeover while the current mold is still in production.
Busting Common Myths About Aluminum Injection Molding
There are some common misconceptions about aluminum injection molding.
Aluminum injection molds are only for low volumes and prototypes.
This is just a stereotype. In fact, depending on the design and the resin used, you could produce up to a million parts from one mold.
Aluminum molds offer limited finishes as compared to steel molds.
This is clearly a myth. Almost any finish that can be applied to steel molds can be used on aluminum molds as well, including various texture and surface grades.
Aluminum injection molding isn’t meant for complex designs.
This is false. Injection molding is a digital manufacturing process and machines use cutting-edge software to ensure accuracy even in the most complex design.
Manufacturing & Engineering Magazine | The Home of Manufacturing Industry News